What is Esomeprazole? Esomeprazole uses!
Esomeprazole belongs to a class of drug know as proton pump inhibitor (PPI) that blocks acid production in the stomach and is used to treat stomach and duodenal ulcers, gastro-esophageal reflux disease (GERD), and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.
Esomeprazole Indications:
- Heartburn,
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD),
- Peptic ulcer disease,
- Active duodenal ulcers,
- Active benign gastric ulcer,
- Erosive oesophagitis,
- Acid-reflux disorders,
- Helicobacter Pylori Eradication,
- Gastrointestinal disorders,
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome,
- Pathological hypersecretory conditions including Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome,
Esomeprazole side effects:
- severe stomach pain,
- diarrhea (watery or bloody),
- seizure (convulsions),
- little or no urination,
- blood in the urine,
- swelling,
- rapid weight gain,
- dizziness,
- fast or irregular heart rate,
- tremors or jerking muscle movements,
- feeling jittery,
- muscle cramps,
- muscle spasm in your hands and feet,
- cough or choking feeling,
- joint pain,
- skin rash,
- headache,
- nausea,
- diarrhea,
- gas,
- constipation,
- dry mouth,
- drowsiness,
Some side effects can be serious but rare. If you experience any of these symptoms, call your doctor immediately, or get emergency medical help:
People who take proton pump inhibitors such as esomeprazole may be more likely to fracture their wrists, hips, or spine than people who do not take one of these medications.
People who take proton pump inhibitors may also develop fundic gland polyps (a type of growth on the stomach lining). These risks are highest in people who take high doses of one of these medications or take them for one year or longer. Talk to your doctor about the risk of taking esomeprazole.
Esomeprazole Dosage:
The recommended adult dose of esomeprazole for GERD is 20 to 40 mg daily of oral or injectable forms.
Or also 20mg orally once/day for 4 weeks; consider an additional 4 weeks of treatment if symptoms do not resolve completely in the first 4 weeks.
Esomeprazole Precautions:
- Tell your doctor or pharmacist whether you are allergic to Esomeprazole or related medicines before taking Esomeprazole or if you have any other allergies. There may be inactive ingredients present in this substance that may cause allergic reactions or other problems.
- Inform your doctor or pharmacist about your medical history, particularly of liver disease, lupus, before taking this drug.
- Signs of a more severe/serious condition may simply be some symptoms. If you have: heartburn with lightheadedness/sweating/dizziness, chest/jaw/arm/shoulder pain (especially with shortness of breath, excessive sweating), unexplained weight gain, get medical attention right away.
- If you have any of these symptoms of a serious condition before self-treating with this drug, get medical attention right away: trouble/pain swallowing food, bleeding vomit, vomit that looks like coffee-colored, bloody or black stools, heartburn for more than 3 months, constant chest pain, wheezing, nausea/vomiting, pain in the stomach.
- Inform your doctor of all the medications you were using before and need before having surgery (including prescription drugs, nonprescription drugs, and herbal products).Your risk of bone fractures can be increased by proton pump inhibitors (such as esomeprazole), particularly with longer use, higher doses, and in older adults.
- Children may be more vulnerable/prone to this drug’s side effects, especially fever, or cough, and nose/throat/airway infections.
Esomeprazole uses in Pregnancy/Breast-feeding:
Esomeprazole and Pregnancy:
The FDA categorizes medications based on their potential risks during pregnancy. Esomeprazole is classified as a category C medication, which means that there are no well-controlled studies in pregnant women, but animal studies have shown potential adverse effects on the fetus.
However, it is crucial to note that categorization alone does not provide a definitive answer on the safety of using esomeprazole during pregnancy. The FDA classification serves as a starting point for healthcare providers to evaluate the potential risks and benefits on an individual basis.
Further research and studies are necessary to fully understand the effects of esomeprazole on pregnancy. Researchers are continually working to gather more data and evidence to provide a clearer picture of the medication’s safety profile during pregnancy.
Healthcare providers may consider alternative treatment options or adjust the dosage of esomeprazole based on the individual’s specific circumstances. Open communication between the healthcare provider and the pregnant individual is vital to ensure the best possible outcome for both the mother and the developing fetus.
Ultimately, the decision to use esomeprazole during pregnancy should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider who can weigh the potential risks and benefits and provide personalized guidance based on the individual’s unique situation.
Esomeprazole and Breast-feeding:

It is not known whether Esomeprazole is excreted in human milk. A decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother. It should only be used upon your doctor’s recommendation.
Esomeprazole Mechanism of Action:
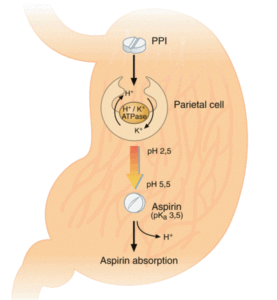
Esomeprazole exerts its stomach acid-suppressing effects by preventing the final step in gastric acid production by covalently binding to sulfhydryl groups of cysteines found on the (H+, K+)-ATPase enzyme at the secretory surface of gastric parietal cells. This effect leads to inhibition of both basal and stimulated gastric acid secretion, irrespective of the stimulus. As the binding of esomeprazole to the (H+, K+)-ATPase enzyme is irreversible and new enzyme needs to be expressed in order to resume acid secretion, esomeprazole’s duration of anti-secretory effect that persists longer than 24 hours.
Storage Required:
- Protect from light and moisture. Store at room temperature.
- Keep Esomeprazole and all medicines out of the reach of children.