What is Amlodipine? Amlodipine uses!
Amlodipine belongs to a class of drugs known as calcium channel blockers. It works by relaxing blood vessels so blood can flow more easily. Amlodipine is used to prevent certain types of chest pain (angina). It may help to increase your ability to exercise and decrease the frequency of angina attacks.
Amlodipine uses also alone or in combination with other medicines to treat high blood pressure (hypertension) in adults and children at least 6 years old. Lowering blood pressure may lower your risk of a stroke or heart attack.
Amlodipine indications:
- Hypertension
- Angina Pectoris
- Hypertensive Renal Disease
- Hypertensive Retinopathy
- Renovascular Hypertension
- Hypertensive Encephalopathy
- Hypertensive Heart Disease
- Prinzmetal’s Angina OR Variant angina
Amlodipine Dosage:
Amlodipine is usually taken once daily.
Initial dose: 5mg orally once a day
Maintenance dose: 5 to 10mg orally once a day
Maximum dose: 10mg/day
Amlodipine uses and Pregnancy:
There is limited evidence regarding use of AMLODIPINE and is generally not preferred as the initial treatment of hypertension in pregnancy. It is best to consult your doctor if you have high blood pressures during pregnancy.
Amlodipine uses and Breast-feeding:

Limited information has shown that levels of amlodipine in milk are usually low and levels of AMLODIPINE in blood of breastfed infants are undetectable. Use of AMLODIPINE during breastfeeding has not been shown to cause any harmful effects in breastfed babies. If AMLODIPINE is required by the mother, it is not a reason to discontinue breastfeeding. If you are a nursing mother, it is best to consult your Obstetrician regarding use of AMLODIPINE.
Amlodipine side effects:
- Swelling (edema)
- Excess fluid in the lungs (pulmonary edema)
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Palpitations
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Flushing
- Abdominal pain
- Sleepiness
- Male sexual disorder
- Drowsiness
- Itching
- Skin rash
- Muscle cramps
- Muscle weakness
Amlodipine Contraindications:
Amlodipine is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to amlodipine or its dosage form components. In addition, amlodipine is relatively contraindicated in patients with cardiogenic shock, severe aortic stenosis, unstable angina, severe hypotension, heart failure, and hepatic impairment. According to the manufacturer’s labeling, patients with severe coronary artery disease may have worsening angina after initiating amlodipine therapy.
In cardiogenic shock, the heart cannot pump effectively, which is exacerbated by inhibiting the influx of calcium ions into cardiac cells. In severe aortic stenosis, amlodipine can cause ventricular collapse and dysfunction. Amlodipine causes a reflexive increase in cardiac contractility in unstable angina, increasing myocardial oxygen demand and worsening ischemia. Amlodipine can further reduce blood pressure, hypo-perfusion to vital organs, and syncope in patients with severe hypotension. Heart failure patients may experience pulmonary edema, shortness of breath, and dyspnea with amlodipine.
Amlodipine Mechanism of action:
Mechanism of action in both Blood pressure and Angina:
Blood Pressure:
Amlodipine is considered a peripheral arterial vasodilator that exerts its action directly on vascular smooth muscle to lead to a reduction in peripheral vascular resistance, causing a decrease in blood pressure. Amlodipine is a dihydropyridine calcium antagonist (calcium ion antagonist or slow-channel blocker) that inhibits the influx of calcium ions into both vascular smooth muscle and cardiac muscle. Experimental studies imply that amlodipine binds to both dihydropyridine and nondihydropyridine binding sites, located on cell membranes. The contraction of cardiac muscle and vascular smooth muscle are dependent on the movement of extracellular calcium ions into these cells by specific ion channels. Amlodipine blocks calcium ion influx across cell membranes with selectivity. A stronger effect of amlodipine is exerted on vascular smooth muscle cells than on cardiac muscle cells. Direct actions of amlodipine on vascular smooth muscle result in reduced blood pressure.
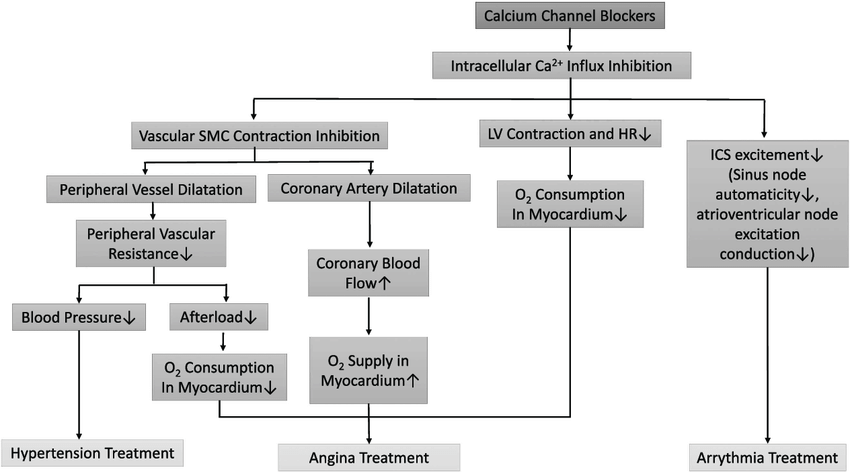
Angina:
The exact mechanism by which amlodipine relieves the symptoms of angina have not been fully elucidated to this date, however, the mechanism of action is likely twofold:
Amlodipine has a dilating effect on peripheral arterioles, reducing the total peripheral resistance (afterload) against which the cardiac muscle functions. Since the heart rate remains stable during amlodipine administration, the reduced work of the heart reduces both myocardial energy use and oxygen requirements.
Dilatation of the main coronary arteries and coronary arterioles, both in healthy and ischemic areas, is another possible mechanism of amlodipine reduction of blood pressure. The dilatation causes an increase in myocardial oxygen delivery in patients experiencing coronary artery spasm (Prinzmetal’s or variant angina) and reduces coronary vasoconstriction caused by smoking.

